
GM/Biotech Crops Report – October 2018
2nd October 2018- GM/Biotech Crops Monthly Reports (BELOW) form part of BCPC’s free three-tier Biotech Crops Info service.
- This service also includes a weekly round-up of news from around the globe – see BCPC Newslink GM Crops section.
- Plus – Free access database on over 300 GM/biotech products covering 23 crops in the global market visit BCPC’s GM/Biotech Crops Manual – Register here for free access.
Already registered? Click here
GM/Biotech Crops Monthly Report October 2018
 |
Viruses to deliver gene therapy |
|---|---|
| Terpenoids on tap Terpenoids are produced by plants in limited quantities but are used by industry for various purposes. Now the on/off switch has been identified promising increased production which makes me think of ’The Sorcerer’s Apprentice’. More Pic: Laura Bernhardt |
 |
 |
Who needs herbicides? Sorghum roots exude sorgoleone, a compound that inhibits the growth of other plants near the sorghum and scientists at the Agricultural Research Service of America are looking at ways of transferring this ability to rice and other crops. Could it also be used as a guide in the search for new residual herbicides? Would these herbicides meet approval thresholds? More Pic: pmanaghan |
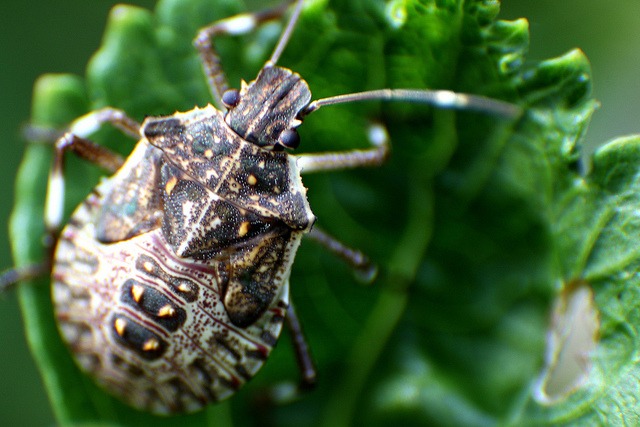
| Taking the waters Stinkbugs are insect pests that attack apples, peaches and tomatoes among other crops and growers use traps to monitor for the presence of the pest to trigger control programmes. Now they have discovered that if they test the rinse water used on the produce for presence of the stinkbug DNA they can detect the pest much earlier and treatment programmes are more effective. More Pic: Dave Hosford |
 |
 |
Better yields with less nitrogen A geneticist at the Chinese Academy of Sciences claims that modern crop varieties absorb nitrogen less efficiently than older varieties and that he knows why. He says that modern varieties have low levels of ‘Factor 4’ and he has bred rice plants with higher levels of this compound. These short plants need lower levels of nitrogen than conventional varieties to produce high yields. More Pic: Audrey Law |
| Covering your tracks CRISPR-Cas9 transgenes can be removed from edited annual plants by sexual segregation but it takes much longer in perennial species. Now researchers in Connecticut have discovered a method of removing them without relying on sexual segregation. Once removed, is there any way of detecting that these plants were ever edited? More Pic:Andrei Zucrev |
 |
 |
Glyphosate ban in Brazil Brazil grows a lot of glyphosate-tolerant GM crops and recently a ban was imposed on the use of glyphosate. However, a Brazilian court has now over-turned the previous injunction before it could take effect and so their agricultural industry is saved. More Pic: Marcus Zorbis |
| A hoary old Chestnut Chestnut trees were once common across America before a fungal disease called Chestnut blight decimated them. Now a team have developed a chestnut tree with heritable blight resistance and are keen to re-establish the trees throughout the land. Could something similar be done for ash and elm in the UK? More Picf: Chris Waits |
 |
 |
Blue-green algae to the rescue |
|---|---|
| Verticillium wilt control Cotton is affected by Verticillium wilt and has few resistant varieties unlike other crops. Now a way of suppressing the disease has been developed using interference RNA (RNAi) to switch off the pathogenic genes in the fungus. More Pic: Kimberly Vardeman |
 |
 |
New anti-depressant drugs Anti-depressant drugs were developed over 30 years ago and no new ones have been released. The site of action of these drugs has been identified as the Delta GABA receptor using gene editing techniques. It is hoped that now the structure of the site of action is known it will aid the development of more targeted drugs with fewer side effects. More Pic: Marc Pether-Longman |
| Less malaria in Africa? Malaria is endemic in Africa and is spread by the bite of the female mosquito. The release of male-sterile mosquitoes has been very effective at reducing mosquito populations in Brazil where it was spreading the Zika virus and now the technique is to be deployed in Africa. More Pic: NIH Image Gallery |
 |
 |
If that doesn’t work, try this Researchers at Imperial College in London have turned off the fertility of female mosquitoes by gene editing and have achieved the complete elimination of mosquito populations in the lab. Could his technique one day be used on wild populations? More Pic: Debris Field |
| A new weapon against antibiotic-resistant bacteria Some bacteria are difficult to kill with antibiotics because they have double cell walls that make it difficult for the drugs to access the cell. Now a molecule labelled G0775 has been synthesised that can easily penetrate the tough outer membrane and facilitate the access of the drugs to the cell within. More Pic:Orthonit |
 |
THE LATEST ADDITIONS TO THE GM/BIOTECH DATABASE ARE:
- MON87708 x MON89788 x A5547-127 – soybean with tolerance of glyphosate, glufosinate and dicamba approved for feed use in Columbia.
- DHA Canola – oilseed rape with modified oil content and tolerance of glufosinate approved for food, feed and environmental use in America and for food use in New Zealand.
- MON87705 x MON87708 x MON89788 – soybean with modified oil content and tolerance of glyphosate and dicamba approved for food and feed use in Mexico and South Africa.
- Bt176 – maize with Lepidopteran insect resistance and tolerance of glyphosate approved for food use in Zambia.
- New stacked event – MIR162 x MON89034 – maize with Lepidopteran insect resistance approved for food, feed and environment use in Argentina and Brazil, food and feed in Mexico and food use in Taiwan.
- MON87427 x MON89034 x MIR162 x MON87411 – maize with resistance to Coleopteran and Lepidopteran insects and tolerance of glyphosate approved for food and feed use in Mexico and food use in Taiwan.
- MS11 – oilseed rape with tolerance of glufosinate approved for food use in Taiwan.
- FG72 x A5547-127 – soybean with tolerance of glyphosate, glufosinate and isoxaflutole herbicides approved for food, feed and processing in the Philippines.
- MON89034 x TC1507 x NK603 x MIR162 – maize with Lepidopteran insect resistance and tolerance of glufosinate and glyphosate approved for food and feed use in Mexico, food use in Taiwan and feed and processing use in Columbia.
- MON87419 – maize with tolerance of glufosinate and dicamba approved for food and feed use in Mexico and for feed use in Columbia.
- MON87751 x MON87701 x MON87708 x MON89788 – soybean with Lepidopteran insect resistance and tolerance of glyphosate and dicamba approved for food and feed use in Mexico and for feed use in Columbia.
- MZIR098 – maize with Coleopteran and lepidopteran insect resistance and tolerance of glufosinate approved for food use in Japan and for feed use in Columbia.
- New stacked event – MON87427 x MON89034 x MON88017 – maize with Coleopteran and Lepidopteran insect resistance and tolerance of glyphosate approved for food, feed and environmental use in Argentina and Japan, food use in Mexico and Taiwan and food and feed use in South Korea.
- New stacked event – 281-24-236 x 3006-210-23 x COT102 – cotton with Lepidopteran insect resistance approved for food, feed and environmental use in Brazil.
- DP305423 x GTS-40-3-2 – soybean with modified oil content and tolerance of glyphosate and sulfonyl urea herbicides approved for commercial use in Brazil.
FOR INSTANT ACCESS TO GM BIOTECH MANUAL CLICK HERE (Registration required)
Already Registered? Click here to access

